“If the past is any guide, we will face a barrage of shocks, both natural and man‐made, in the coming years. In just the past five years, we have seen a major earthquake in Haiti; drought in the Horn of Africa; earthquake, tsunami, and nuclear crisis in Japan; and conflicts that have left millions of >> Read more
Highlights From Conference Briefs 12 and 14: Building Resilience In The Face Of Conflict
In the past few decades, food-related challenges like climate change and food and nutrition security coupled with other social and political issues have led to conflict and unrest on both the national and regional scale. Climatic shocks are considered to be one of the root causes of conflict, especially in resource-constrained settings. At the same time, conflicts tend to exacerbate existing vulnerability, leading to poverty‐conflict traps at the household, community, and national levels. In their conference brief, Margherita Calderone, Derek Headey, and Jean-François Maystadt review the research about the impact of climate change >> Read more
Pacific voices to be heard at Global Conference on Building Resilience to Food and Nutrition Security
Voices from Small Island Developing States including the Pacific and the Caribbean will be heard at the High Level Panel on Global Conference on Building Resilience to Food and Nutrition Security which begins today in the Ethiopian capital, Addis Ababa. The Director for the Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation (CTA), Michael Hailu >> Read more
2020 Conference officially underway
The 2020 Conference on "Building Resilience for Food and Nutrition Security" officially kicked off in Addis Ababa this morning with the first round of side events. The three-day event, which is being attended by more than 800 experts and practitioners from food, nutrition, health, agriculture, humanitarian, and related development sectors, aims to incorporate resilience into >> Read more
Highlights from Conference Brief 5: Are Shocks Actually on the Rise?
From extreme weather events to rising and highly volatile food prices, poor and vulnerable populations are subject to a bevy of shocks that threaten their basic food and nutrition security. In the face of global climate change and other recent food price spikes, it seems to many that such events are occurring more and more >> Read more
Highlights from 2020 Conference Brief 7: Nongovernmental organizations’ approaches to resilience programming
Stories of nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) providing emergency relief in the aftermath of natural disasters and other humanitarian crises are familiar parts of the news. When NGOs such as CARE or Mercy Corps support medical services in South Sudan or bring food to people affected by Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines, we are not surprised. Less >> Read more
Highlights from Conference Brief 4: Local sources of resilience
Before government programs and international aid efforts, people coped with disasters, famine, conflicts, and other shocks by coming together as a community and relying on their networks—in other words, using social capital. Social capital, in the form of community-based organizations and social networks, has traditionally played an important, but largely unexplored, role in building resilience. >> Read more
Highlights from Conference Brief 18: Strengthening the links between resilience and nutrition
In the field of food policy, nutrition and resilience are strongly interlinked conceptually—and now Charlotte Dufour, Domitille Kauffmann, and Neil Marsland are trying to bind the two much more tightly in practice. Resilience, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), is “the ability to prevent disasters and crises as well >> Read more
Highlights from Conference Briefs 10, 17 and 19
There is a wide recognition that building the resilience of the rural poor—the most vulnerable group—requires helping the affected recover from various shocks, such as weather and nutritional shocks.
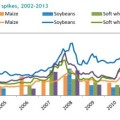
Highlights from Conference Brief 16: Building a resilient global food system by lowering food price spikes and volatility
Why should we be concerned about volatility and spikes in global food prices, particularly since they have subsided in recent years?